CBSE Test Paper 01
Chapter 8 Gravitation
- The direction of the universal gravitational force between particles of masses and is: 1
- towards
- towards on and towards on .
- towards the center of the earth
- towards
- The space shuttle releases a 470-kg communications satellite while in an orbit that is 280 km above the surface of the Earth. A rocket engine on the satellite boosts it into a geosynchronous orbit, which is an orbit in which the satellite stays directly over a single location on the Earth. How much energy did the engine have to provide? 1
- 1.09 J
- 1.29 J
- 1.39 J
- 1.19 J
- Time period of an earth satellite very close to the surface of earth is given by 1
- A body weighs 63 N on the surface of the earth. What is the gravitational force on it due to the earth at a height equal to half the radius of the earth? 1
- 18 N
- 128 N
- 28 N
- 180 N
- Two stars each of one solar mass (= 2 kg) are approaching each other for a head on collision. When they are a distance km, their speeds are negligible. What is the speed with which they collide? The radius of each star is 104 km. assume the stars to remain undistorted until they collide. (Use the known value of G) 1
- 2.6 m/s
- 1.6 m/s
- 2.2 m/s
- 2.8 m/s
-
Do the friction of force and other contact forces arise due to gravitational attraction? If not, then what is the origin of these forces? 1
-
Define the effect of the shape of the earth on the value of g. 1
-
A thief with a box in his hand jumps from the top of a building. What will be the load experienced by him during the state of free fall? 1
-
If an object at the altitude of the space shuttle’s orbit, about 400 km about the earth’s surface, then find out the free fall acceleration of that object. 2
-
Derive an expression for work done against gravity. 2
-
State three essential requisites of geostationary satellite. 2
-
Find the distance of a point from the earth’s centre where the resultant gravitational field due to the earth and the moon is zero. The mass of the earth is 6.0 1024 kg and that of the moon is 7.4 1022 kg. The distance between the earth and the moon is 4.0 106 km. 3
-
Two uniform solid spheres of radii R and 2R are at rest with their surfaces just touching. Find the force of gravitational attraction between them if density of spheres be P? 3
-
Obtain an expression for escape velocity from energy considerations. 3
-
A spaceship is stationed on Mars. How much energy must be expended on the spaceship to launch it out of the solar system? Mass of the space ship = 1000 kg; mass of the Sun = kg; mass of mars = kg; radius of mars = 3395 km; radius of the orbit of mars = ; . 5
CBSE Test Paper 01
Chapter 8 Gravitation
Answer
-
-
towards on and towards on .
Explanation: since gravitational force is attractive in nature, so if there are two particles of m1 & m2 .
So One Force will be on m1 which will be directed towards m 2. i.e
And other force wiil be on m2 which will be directed towards m 1 i.e
Clearly, It can be seen that Because thsese forces are attracted to each other and direction of each force is opposite to other one.
-
-
- 1.19 J
Explanation: Period of rocket in geosynchronous orbit is same as that of the earth:
That is T = 1day = 24hours = 24 60 60 sec = 8.64 104 s
From Keplers 3rd law
T2 = KEr3GS
Where KE = = 9.89 10-14s2/m3
Therefore the geosynchronus radius is
Because the initial position before the boost is 280 km = 2.8 105 m
and the radius of the Earth is 6,370 km = 6.37 106 m
Therefore ri = RE + 2.80 105 m = 6.65 106 m
The total energy needed to boost the satellite at the geosynchronus radius is the difference of total energy before and after the boost
= 1.19 1010J
- 1.19 J
-
Explanation: It is the time taken by satellite to go once around the earth
Since Satellite is very close to the surface of earth, So Here, we can take r=R(Radius of earth)
As
-
- 28 N
Explanation:
Given, h =
Let m = mass of the body
If W and Wh be its weight at earth’s surface and at a height h above earth’s surface, then
W = mg
- 28 N
-
- 2.6 m/s
Explanation: Let and be the velocities of two stars when they collide.
According to the law of conservation of momentum,
According to law of conservation of energy,
We Have
Mass of the star, M = 2 1030 kg
Distance between the stars, r1 = 109 km = 1012 m
Radius of star, r = 104km = 107m
The distance between two stars when they collide is,
2r = 2 107m
Speed with which the stars collide is given by,
- 2.6 m/s
-
No, the origin of forces of friction or other contact forces arises from electromagnetic force. The origin of electromagnetic force is due to attraction/repulsion between particles.
-
The value of g decreases from poles to the equator. Therefore, at the surface of the earth, g is maximum at the poles and minimum at the equator
-
The load experienced by him will be zero because during the state of free fall, the acceleration is equal to the acceleration due to gravity. So, the thief will be in the state of weightlessness.
-
= =
If the object is at height h above the earth’s surface, then
= 8.70 m/s2 -
Potential energy of the body on the surface of the earth =
Potential energy at a from the surface of the earth = –
–
= –
= =
= = -
- The period of revolution of a satellite around the earth should be same as that of earth about its own axis (T=24 hrs)
- The sense of rotation of satellite should be same as that of the earth about its own axis i.e. from west to east in anti-clockwise direction.
- It should orbit in the equatorial plane and have same speed as that of earth.
-
The point must be on the line joining the centres of the earth and the moon. If the distance of the point from the earth is x, the distance from the moon is . The magnitude of the gravitational field due to the earth is
Magnitude of the gravitational field due to the moon is
These fields are in opposite directions.
=
=
-
Two spheres of density p and radii R and 2R
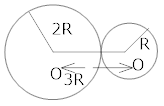
Given , density of each sphere is ρ
For finding mass of each sphere , we have to find volume of each
Volume of sphere of radius R , V₁ = R³
volume of sphere of radius 2R, V₂ = (2R)³ =
Now, mass of 1st sphere, M₁ = V₁ ρ [ mass = density volume ]
=
mass of 2nd sphere, M₂ = V₂ ρ =
= 2R + R = 3R
Now, Gravitational force act between M₁ and M₂ , F =
=
=
=
Hence, force between them, F = -
Consider a body of mass m projected from the surface of Earth with a speed ves, which is just sufficient to take the body up to infinite distance away.
–
Total energy of the body at the surface of Earth –
When the body reaches infinity, its final velocity and hence kinetic energy is zero i.e.= 0
Also = –= 0
Total energy of body at infinity = 0
– = 0
=
As g = ,
-
Mass of the spaceship, mS = 1000 kg
Mass of the Sun, M = kg
Mass of Mars, mM = kg
Orbital radius of Mars, R = = m
Radius of Mars, r = 3395 km =
Universal gravitational constant,
Potential energy of the spaceship due to the gravitational attraction of the Sun
Potential energy of the spaceship due to the gravitational attraction of Mars
Since the spaceship is stationed on Mars, its velocity and hence, its kinetic energy will be zero.
Total energy of the spaceship
The negative sign indicates that the system is in bound state.
Energy required for launching the spaceship out of the solar system
= – (Total energy of the spaceship)